Exemple de configuration simple
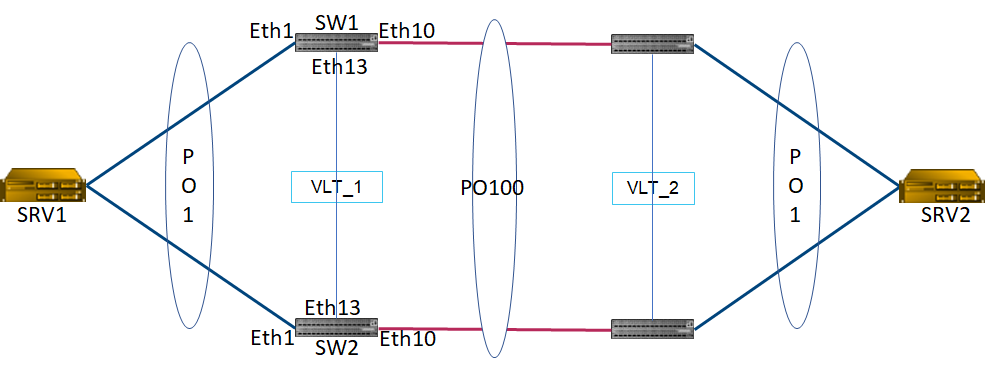
Soit un domaine VLT interconnecté en L2, via une interco LACP à un autre domaine VLT.
Pas de routage activé sur les équipements. On considère que le SRV1 et SRV2 ont des vlans en communs.
On aura donc un trunk avec les n Vlans nécessaires déclarés sur le PO1 (attachement du serveur) mais aussi sur le PO100 qui sert à l’interco des deux domaines VLT.
On commence par interconnecter les deux ports OOB pour avoir un lien de HeartBeat entre les deux swicths du même domaine VLT
| SW1 | SW2 |
| interface mgmt1/1/1 no shutdown no ip address dhcp ip address 10.10.10.1/30 no ipv6 enable ! | interface mgmt1/1/1 no shutdown no ip address dhcp ip address 10.10.10.2/30 no ipv6 enable ! |
Déclaration du VLT entre SW1 et SW2
| SW1 | SW2 |
| vlt-domain 1 backup destination 10.10.10.2 discovery-interface ethernet1/1/13 primary-priority 4096 vlt-mac xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx | vlt-domain 1 backup destination 10.10.10.1 discovery-interface ethernet1/1/13 primary-priority 8192 vlt-mac xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx |
Si vous n’utilisez pas le mgmt port, ne déclarez pas de backup destination.
On rajoute les vlans nécessaires
| SW1 | SW2 |
| interface vlan10 description “VLAN10” no shutdown | interface vlan10 description “VLAN10” no shutdown |
| interface vlan12 description “VLAN12” no shutdown | interface vlan12 description “VLAN12” no shutdown |
On configure les interfaces d’attachement au serveur SRV1 (mais ça pourrait être un switch). Dans le cas d’un serveur attention au type de teaming/bonding, dans le cas présent on est sur un teaming de type switch dépendant.
On en profite pour creer le Port-Channel 1, et on laisse passer les VLANs 10, 12 dans trunk.
| SW1 | SW2 |
| interface ethernet1/1/1 description “Vers SRV1_Port1” no shutdown channel-group 1 mode active no switchport flowcontrol receive off | interface ethernet1/1/1 description “Vers SRV1_Port2” no shutdown channel-group 1 mode active no switchport flowcontrol receive off |
| interface port-channel1 description “PO1_SRV1_P1” no shutdown switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,12 vlt-port-channel 1 | interface port-channel1 description “PO1_SRV1_P2” no shutdown switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,12 vlt-port-channel 1 |
On configure ensuite les interfaces et le port channel à destination du second domaines VLT. On laisse passer dans le trunk du port channel 100 les Vlans 10, 12.
| SW1 | SW2 |
| interface ethernet1/1/10 description “Vers VLT2_SW1_Port10” no shutdown channel-group 100 mode active no switchport flowcontrol receive off | interface ethernet1/1/10 description “Vers VLT2_SW2_Port10” no shutdown channel-group 100 mode active no switchport flowcontrol receive off |
| interface port-channel100 description “PO100_VLT2_P10” no shutdown switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,12 vlt-port-channel 100 | interface port-channel100 description “PO100_VLT2_P10” no shutdown switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,12 vlt-port-channel 100 |
On répéte l’action en adaptant sur le second domaines VLT.
Attention les domaines VLTs doivent avoir des ID unique, donc la déclaration du second domaine VLT se fera comme suit, sur les deux switchs du VLT domaine 2
vlt-domain 2
backup destination xx.xx.xx.xx
discovery-interface ethernet1/1/13
primary-priority 4096 [8192]
vlt-mac xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
